การผลิตโปรตีนไฮโดรไลเสตจากปลา
โปรตีนไฮโดรไลซ์จากผลผลิตพลอยได้จากปลาทำให้ได้ผลผลิตเป็นผลิตภัณฑ์ที่มีมูลค่าสูงหลายประเภทจากวัตถุดิบของคุณ 100% ในขณะเดียวกันก็ช่วยลดผลกระทบต่อสิ่งแวดล้อมของโรงงานด้วย ราคาตลาดที่สูงของโปรตีนไฮโดรไลซ์ทำให้ไฮโดรไลซิสเป็นทางเลือกที่น่าสนใจอย่างมากแทนการผลิตปลาป่นแบบดั้งเดิม
มีการใช้กระบวนการที่แตกต่างกันสองกระบวนการสำหรับการไฮโดรไลซิสโปรตีนจากปลา: การไฮโดรไลซิสด้วยเอนไซม์และการไฮโดรไลซิสด้วยกรด (ซิเลจ) Alfa Laval นำเสนอโซลูชันการประมวลผลที่ครบถ้วนสำหรับทั้งคู่


เปลี่ยนวัตถุดิบมูลค่าต่ำให้เป็นไฮโดรไลเสทปลาที่มีมูลค่าสูง
การผลิตไฮโดรไลเสทปลาโดยใช้กระแสด้านข้างจากการดำเนินการแล่เนื้อปลา เช่น หัวปลา หนัง กระดูก และอวัยวะภายใน ทำให้เกิดเปปไทด์และกรดอะมิโนที่มีมูลค่าสูง กระบวนการนี้ยังปล่อยน้ำมันปลาและสารอาหารอันทรงคุณค่าอื่นๆ ออกจากวัตถุดิบด้วย กระบวนการไฮโดรไลซิสทำให้โปรตีนแตกตัวเป็นโปรตีนเปปไทด์ที่ละลายน้ำได้ซึ่งมีคุณค่าทางโภชนาการและคุณภาพสูงกว่าเมื่อเทียบกับโปรตีนปลาป่นแบบดั้งเดิม
โปรตีนไฮโดรไลเสตที่ได้นี้สามารถนำไปใช้ในโภชนาการการกีฬา เครื่องสำอาง อาหารเพื่อสุขภาพ และการใช้อาหารสัตว์ ผลิตภัณฑ์ประกอบด้วยผลิตภัณฑ์เสริมอาหารคอลลาเจน โปรตีนเปปไทด์สกัดบริสุทธิ์ น้ำซุป น้ำปลา และสารปรุงแต่งรสสำหรับอาหารปลาและอาหารสัตว์เลี้ยง
นอกจากนี้ การไฮโดรไลซ์ของเหลือจากการแปรรูปปลายังช่วยลดของเสียและนำเสนอโซลูชั่นที่ยั่งยืนสำหรับความท้าทายอย่างต่อเนื่องในการจัดการของเสียในอุตสาหกรรมปลา
การไฮโดรไลซิสด้วยเอนไซม์
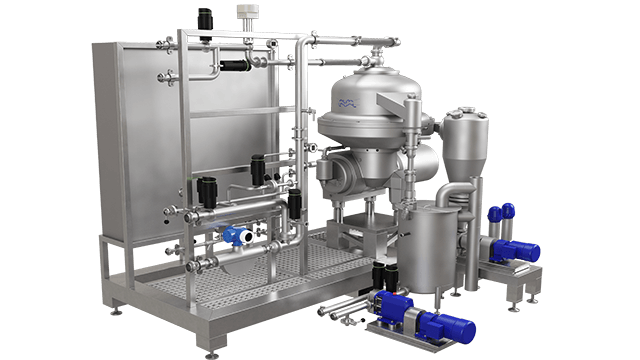
การแปรรูปไฮโดรไลเสทปลาด้วยเอนไซม์เป็นกระบวนการทำให้โปรตีนปลาเข้มข้นที่ต้องการสำหรับผลผลิตพลอยได้ของปลาที่ได้จากการแล่เนื้อ ใช้ในการผลิตคอลลาเจนและเปปไทด์คุณภาพสูง ส่วนผสมปรุงรสสำหรับน้ำซุปและน้ำปลา และสารดึงดูดสำหรับอาหารปลาและอาหารสัตว์เลี้ยง
ประโยชน์หลักสองประการของการไฮโดรไลซิสด้วยเอนไซม์เหนือการไฮโดรไลซิสด้วยกรดคือคุณภาพของน้ำมันและโปรตีนที่ได้ที่สูงขึ้น อีกทั้งความเป็นไปได้ในการปรับแต่งรสชาติและการทำงานของผลิตภัณฑ์โปรตีนขั้นสุดท้ายโดยการเลือกเอนไซม์ที่แตกต่างกัน นอกจากนี้ การประมวลผลด้วยเอนไซม์ยังทำให้สามารถแยกกระดูกออกจากน้ำมันและโปรตีนได้ ช่วยให้ผู้ผลิตสามารถสร้างผลิตภัณฑ์แคลเซียมที่สามารถขายแยกได้ จึงช่วยเพิ่มมูลค่ารวมได้สูงสุด
Alfa Laval นำเสนอสายการผลิตที่สมบูรณ์สำหรับการไฮโดรไลซิสด้วยเอนไซม์ และผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้านการใช้งานของเรายินดีที่จะช่วยเหลือคุณตลอดกระบวนการทั้งหมดในการออกแบบและใช้งานโซลูชันที่ปรับให้เหมาะกับความต้องการเฉพาะของคุณ
คำอธิบายกระบวนการ
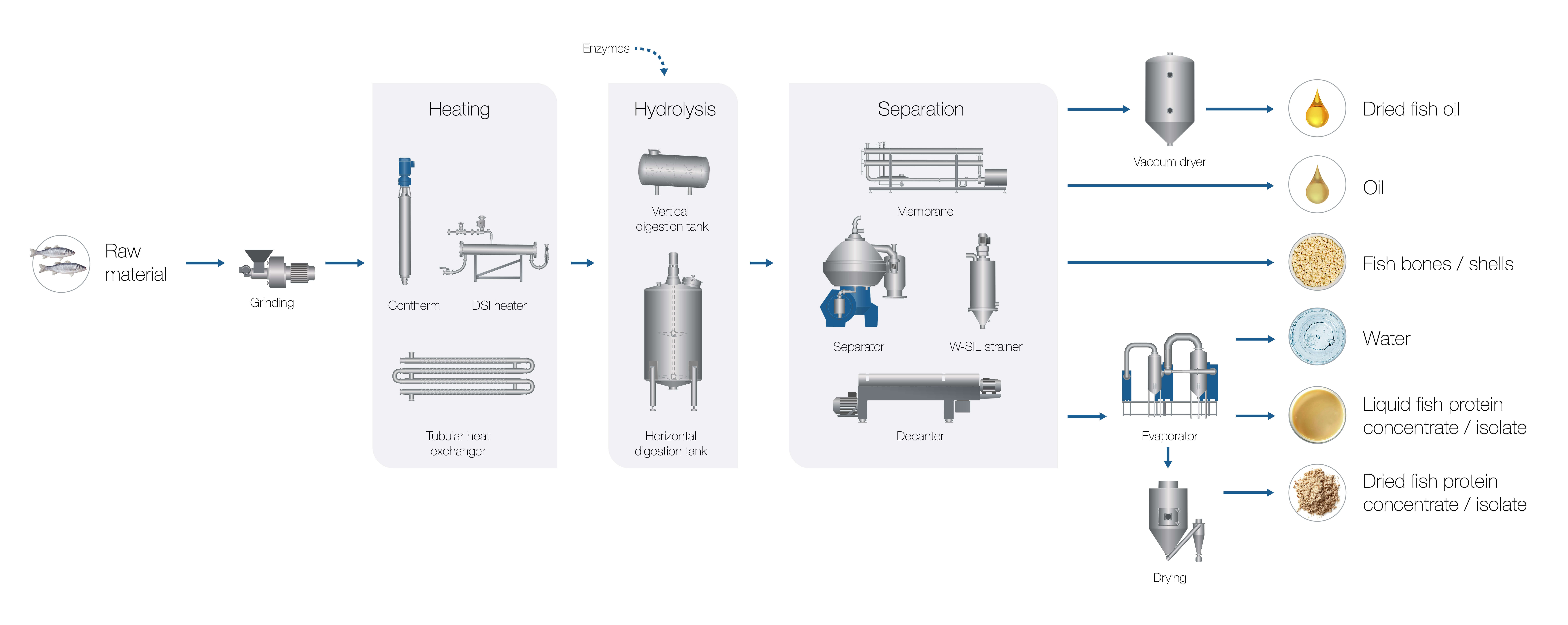
- ในขั้นตอนแรกของกระบวนการ วัตถุดิบจะสับละเอียดเพื่อปรับปรุงการทำงานของเอนไซม์ เอนไซม์จะถูกเติมลงในปลาสับ และส่วนผสมจะถูกให้ความร้อนจนถึงอุณหภูมิที่เหมาะสมสำหรับเอนไซม์ที่เลือก หากจำเป็น จะปรับระดับ pH เพื่อเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพการย่อยสลาย จะเติมเอนไซม์ก่อนเมื่อกระบวนการไฮโดรไลซิสเริ่มต้นเพื่อการควบคุมกระบวนการย่อยสลายสูงสุด ทำให้ติดตามเวลาการย่อยได้ง่าย และช่วยให้มั่นใจได้ว่าวัตถุดิบทั้งหมดได้รับการประมวลผลในระยะเวลาเท่ากัน
- ส่วนผสมจะปฏิกิริยาตามระยะเวลาที่กำหนด โดยทั่วไปคือ 1-3 ชั่วโมง ขึ้นอยู่กับปัจจัยต่างๆ เช่น วัตถุดิบ เอนไซม์ และผลลัพธ์ที่ต้องการ
- เมื่อได้ระดับไฮโดรไลซิสตามที่ต้องการแล้ว จะยับยั้งเอนไซม์โดยการให้ความร้อน ขั้นตอนการให้ความร้อนขั้นที่สองยังปรับอุณหภูมิให้เหมาะสมสำหรับขั้นตอนการแยกครั้งต่อไป เพื่อให้มั่นใจว่าจะได้น้ำมันสูงสุด
- ในขั้นตอนการแยกส่วน อนุภาคก้างที่ไม่ได้ย่อยจะกำจัดออกก่อนที่จะแปรรูปสารละลายในเครื่องแยกส่วนหรือดีแคนเตอร์ โดยที่น้ำมันจะแยกออกจากโปรตีน การเลือกใช้อุปกรณ์แยกขึ้นอยู่กับความเข้มข้นของสารละลาย เครื่องแยกส่วนใช้สำหรับสารละลายที่มีของแข็งน้อยกว่า 5% และดีแคนเตอร์ใช้เมื่อความเข้มข้นสูงกว่า เนื่องจากกระบวนการไฮโดรไลซิสจะเปลี่ยนโปรตีนที่ไม่ละลายน้ำให้เป็นโปรตีนที่ละลายน้ำได้ ปริมาณโปรตีนมากกว่า 90% จึงอยู่ในส่วนของน้ำที่ออกจากเครื่องแยกส่วนหรือดีแคนเตอร์ ส่วนนี้สามารถประมวลผลเพิ่มเติมได้ในระบบเมมเบรนโดยใช้อัลตรา-และนาโนฟิลเตรชันเพื่อแยกเปปไทด์จำเพาะ
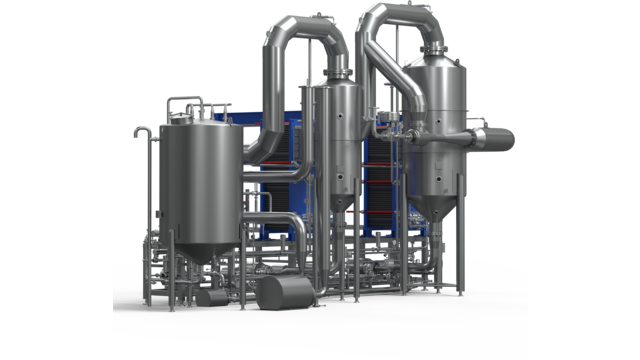
- สุดท้ายนี้ สารละลายโปรตีนจะต้องผ่านระบบการระเหยและอาจต้องใช้เครื่องอบแห้ง ขึ้นอยู่กับข้อกำหนดปริมาณน้ำ เพื่อผลิตผลิตภัณฑ์ขั้นสุดท้าย

วัตถุดิบ
- ผลผลิตพลอยได้จากการตัดเนื้อปลา
- ปลาทั้งตัวที่มีขนาดเล็กกว่าซึ่งไม่เหมาะสำหรับการบริโภคโดยตรง
การแปรรูปซิเลจ (การไฮโดรไลซิสด้วยกรด)
การผลิตซิเลจปลาด้วยสัตว์น้ำจากฟาร์มที่ตาย เศษปลา และผลผลิตพลอยได้ เช่น หัว หนัง และอวัยวะภายใน ช่วยให้โรงงานแปรรูปปลา ฟาร์มปลา และการประมงสามารถใช้วัตถุดิบให้เกิดประโยชน์สูงสุด และปฏิบัติตามกฎระเบียบการปล่อยของเสียที่เข้มงวดมากขึ้น ซิเลจปลาเป็นโซลูชันการจัดการของเสียที่เหมาะสมที่สุดสำหรับเรือประมงขนาดเล็ก ฟาร์มปลา และโรงงานแปรรูปปลา ซึ่งไม่สามารถติดตั้งสายไฮโดรไลซิสด้วยเอนไซม์ได้
ซิเลจปลาผลิตโดยการผสมวัตถุดิบกับกรด ซึ่งทำได้ที่ฟาร์มเลี้ยงปลา บนเรือประมง หรือที่โรงแล่ปลาซึ่งมีปริมาณผลพลอยได้จำกัด การเปลี่ยนผลพลอยได้ให้เป็นหญ้าหมักหมายความว่าสามารถรวบรวมและจัดเก็บได้นานถึงหกเดือนก่อนนำไปแปรรูปต่อ ซึ่งช่วยลดฤดูกาลในการดำเนินงานต่างๆ ได้อย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ หลังจากแปรรูปหญ้าหมักแล้ว เศษโปรตีนสามารถนำมาใช้ในอาหารปลาและอาหารสัตว์เลี้ยง เป็นตัวเสริมทางโภชนาการในการผลิตก๊าซชีวภาพ หรือเป็นปุ๋ยอินทรีย์
Alfa Laval นำเสนอโซลูชั่นระบบครบวงจรสำหรับการแปรรูปปลาหมักและการสกัดโปรตีนจากปลา ทีมผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้านการใช้งานของเราสนับสนุนคุณตลอดกระบวนการทั้งหมดในการออกแบบและใช้งานโซลูชันที่ปรับให้เหมาะกับความต้องการเฉพาะของคุณ
วัตถุดิบ
- เศษปลาและผลพลอยได้
- สัตว์น้ำจากฟาร์มที่ตาย (สำหรับใช้ในการผลิตปุ๋ยหรือก๊าซชีวภาพ ไม่ใช้เป็นอาหารสัตว์)
คำอธิบายกระบวนการ
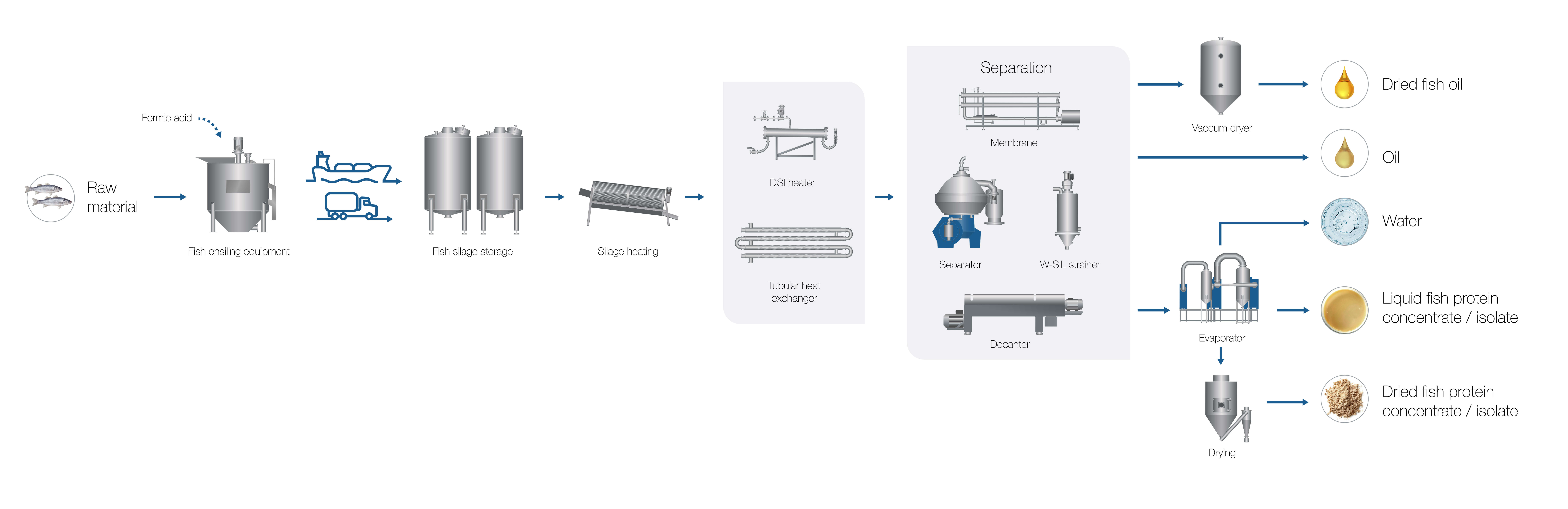
- ในขั้นตอนแรกของกระบวนการ วัตถุดิบจะถูกสับและผสมกับกรด (โดยปกติจะเป็นกรดฟอร์มิกหรือกรดอินทรีย์อื่น) เพื่อลดระดับ pH ลงเหลือ 3.5 โดยทั่วไปจะทำในหน่วยขนาดเล็กที่มีปั๊มถังและปั๊มสับในตัว
- หลังจากผ่านไปไม่กี่ชั่วโมง เนื้อปลาก็จะกลายเป็นของเหลว สาเหตุหลักมาจากการทำงานของเอนไซม์ภายในปลา ระดับ pH ต่ำจะช่วยเร่งการสลายและรักษาซิเลจระหว่างการเก็บรักษา หลังจากนั้น ส่วนผสมสามารถเก็บไว้ได้หลายเดือนก่อนที่จะรวบรวมและแปรรูปที่สถานที่กลาง
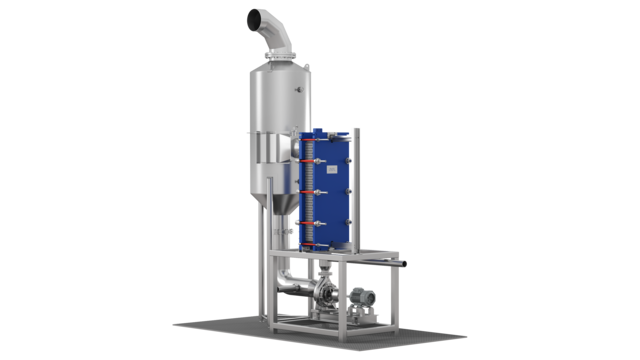
- เมื่อได้รับหญ้าหมักที่โรงงานแปรรูป จะมีการคัดกรองเพื่อกำจัดสิ่งแปลกปลอม เช่น พลาสติก เศษไม้ และหิน
- ก่อนขั้นตอนการแยก หญ้าหมักจะถูกให้ความร้อนเพื่อสลายอิมัลชันไขมันและลดความหนืดของน้ำมัน ซึ่งจะช่วยปรับเงื่อนไขสำหรับการแยกให้เหมาะสมที่สุด เพื่อให้มั่นใจได้ถึงผลผลิตน้ำมันสูงสุด
- ในขั้นตอนการแยกส่วน น้ำมันจะแยกออกจากโปรตีนในเครื่องแยกส่วนหรือดีแคนเตอร์ ความเข้มข้นของสารละลายเป็นตัวกำหนดการเลือกอุปกรณ์แยกส่วน สำหรับสารละลายที่มีปริมาณของแข็งแขวนลอยน้อยกว่า 5% จะใช้เครื่องแยกส่วน ในขณะที่จะใช้ดีแคนเตอร์เมื่อความเข้มข้นสูงกว่า กระบวนการไฮโดรไลซิสจะเปลี่ยนโปรตีนที่ไม่ละลายน้ำให้เป็นโปรตีนที่ละลายน้ำได้ ซึ่งหมายถึงโปรตีนมากกว่า 90% อยู่ในส่วนของน้ำที่ออกจากเครื่องแยกส่วนหรือดีแคนเตอร์
- ในขั้นตอนสุดท้าย สารละลายโปรตีนจะถูกทำให้เข้มข้นในระบบระเหยหรือทำให้แห้งในระบบอบแห้ง
วัตถุดิบสำหรับไบโอดีเซลและ HVO
ตลาดไบโอดีเซลและ HVO ที่เฟื่องฟูส่งผลให้ความต้องการน้ำมันและไขมันมีการเติบโตอย่างมาก น้ำมันที่ผลิตในกระบวนการซิเลจไม่เหมาะสำหรับการบริโภคของมนุษย์ แต่เป็นวัตถุดิบที่น่าสนใจสำหรับไบโอดีเซลและ การผลิต HVO
นอกเหนือจากสายการผลิตหญ้าหมักแล้ว Alfa Laval ยังมีระบบการบำบัดวัตถุดิบเบื้องต้นที่ครบถ้วน ซึ่งกำจัดฟอสเฟอร์ โลหะปริมาณน้อย คลอไรด์ โพลีเอทิลีน และสิ่งสกปรกอื่นๆ
ติดต่อผู้เชี่ยวชาญของเราเพื่อเรียนรู้ว่าคุณสามารถใช้ประโยชน์จากโอกาสในภาคเชื้อเพลิงชีวภาพได้อย่างไร
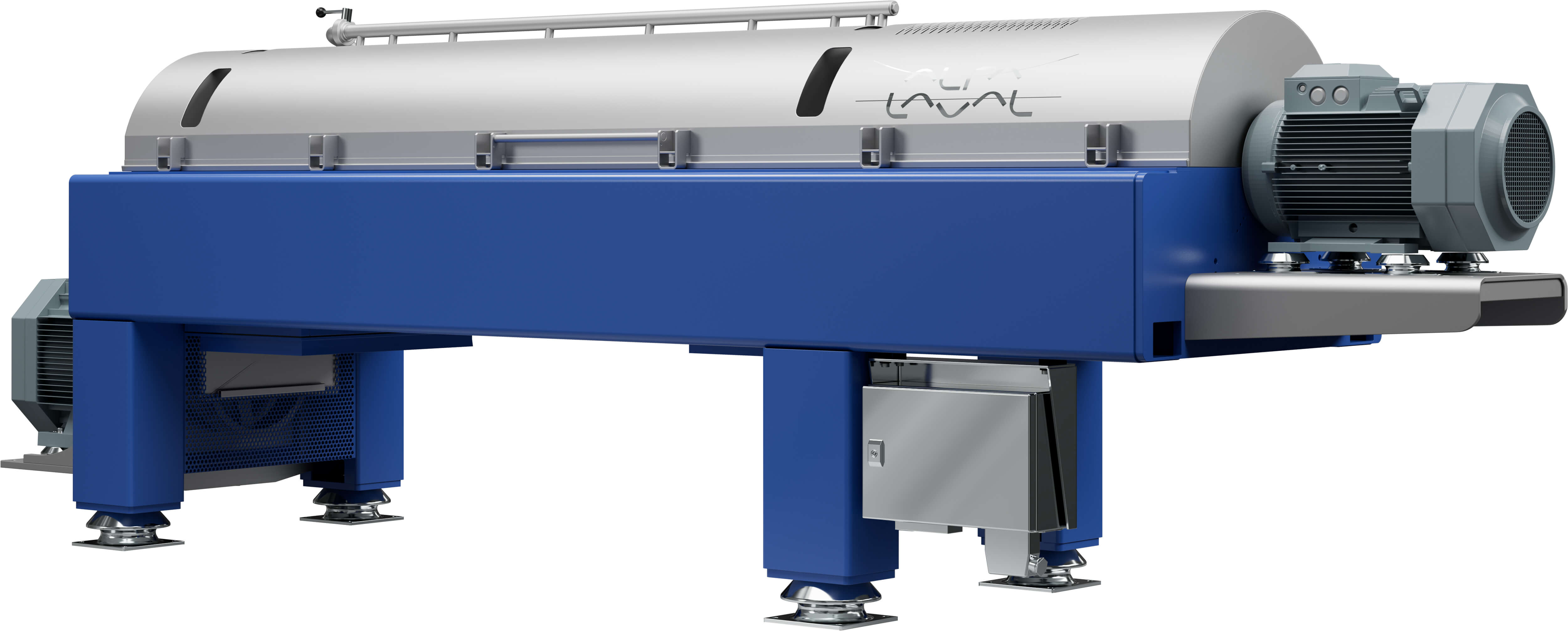


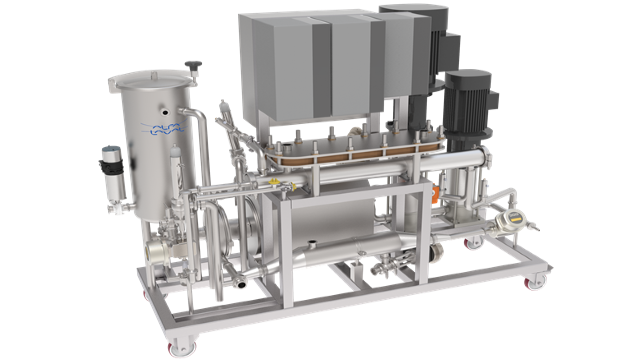
Alfa Laval Foodec Oil Plus – สร้างมาตรฐานใหม่สำหรับการสกัดน้ำมัน
Alfa Laval Foodec Oil Plus ใหม่กำลังปฏิวัติการผลิตน้ำมันปลา ด้วยการออกแบบที่เป็นนวัตกรรม Foodec Oil Plus จึงสกัดน้ำมันได้มากกว่าโซลูชันอื่นๆ ช่วยให้มั่นใจได้ถึงการใช้วัตถุดิบให้เกิดประโยชน์สูงสุด
- ผลผลิตน้ำมันสูงสุดด้วยดีแคนเตอร์ที่มีการออกแบบใหม่เป็นพิเศษ
- น้ำมันบริสุทธิ์มาก โดยต้องผ่านกระบวนการเพิ่มเติมเพียงเล็กน้อย
- ใช้งานและบำรุงรักษาง่าย
- ต้นทุนรวมในการเป็นเจ้าของต่ำและระยะเวลาคืนทุนสั้น ซึ่งมักจะน้อยกว่า 1 ปี
- มีจำหน่ายในรูปแบบสกิดที่ใช้งานได้ทันที
- การเปลี่ยนแปลงในกระบวนการที่มีอยู่ของคุณเพียงเล็กน้อย มีเพียงส่วนประกอบใหม่เพียงชิ้นเดียว
บริการที่รวดเร็วและมีความสามารถ
ด้วย Alfa Laval ในฐานะพันธมิตรบริการที่เชื่อถือได้ คุณสามารถไว้วางใจความช่วยเหลือที่รวดเร็วและมีความสามารถได้ทุกที่ทุกเวลาที่คุณต้องการ แม้แต่ในสถานที่ห่างไกลที่สุด เครือข่ายสำนักงานบริการทั่วโลกของเราให้การสนับสนุนอย่างมืออาชีพตลอดทุกขั้นตอนของการดำเนินงานของคุณ รวมถึงการแก้ไขปัญหา การบำรุงรักษาตามปกติ การตรวจสอบประสิทธิภาพขั้นสูง และการบำรุงรักษาเชิงคาดการณ์
ด้วยการใช้บริการระยะไกลของเรา เราจึงสามารถให้ความช่วยเหลือได้ทันทีผ่านช่องทางดิจิทัล ช่างเทคนิคภาคสนามของเราสามารถจัดส่งไปยังไซต์งานหรือท่าเรือทั่วโลกได้อย่างรวดเร็ว หากคุณต้องการความช่วยเหลือนอกสถานที่
เครือข่ายท้องถิ่นที่แข็งแกร่งของเราทำให้เราเป็นผู้ให้บริการที่เหมาะสมที่สุดสำหรับบริษัทที่มีการดำเนินงานทั่วโลก ส่งเสริมความร่วมมือที่ใกล้ชิดยิ่งขึ้น และลดภาระด้านการบริหาร มอบความไว้วางใจให้กับ Alfa Laval สำหรับโซลูชันการบริการที่ครอบคลุม รับประกันการทำงานที่ไม่หยุดชะงักไม่ว่าจะอยู่ที่ใดก็ตาม